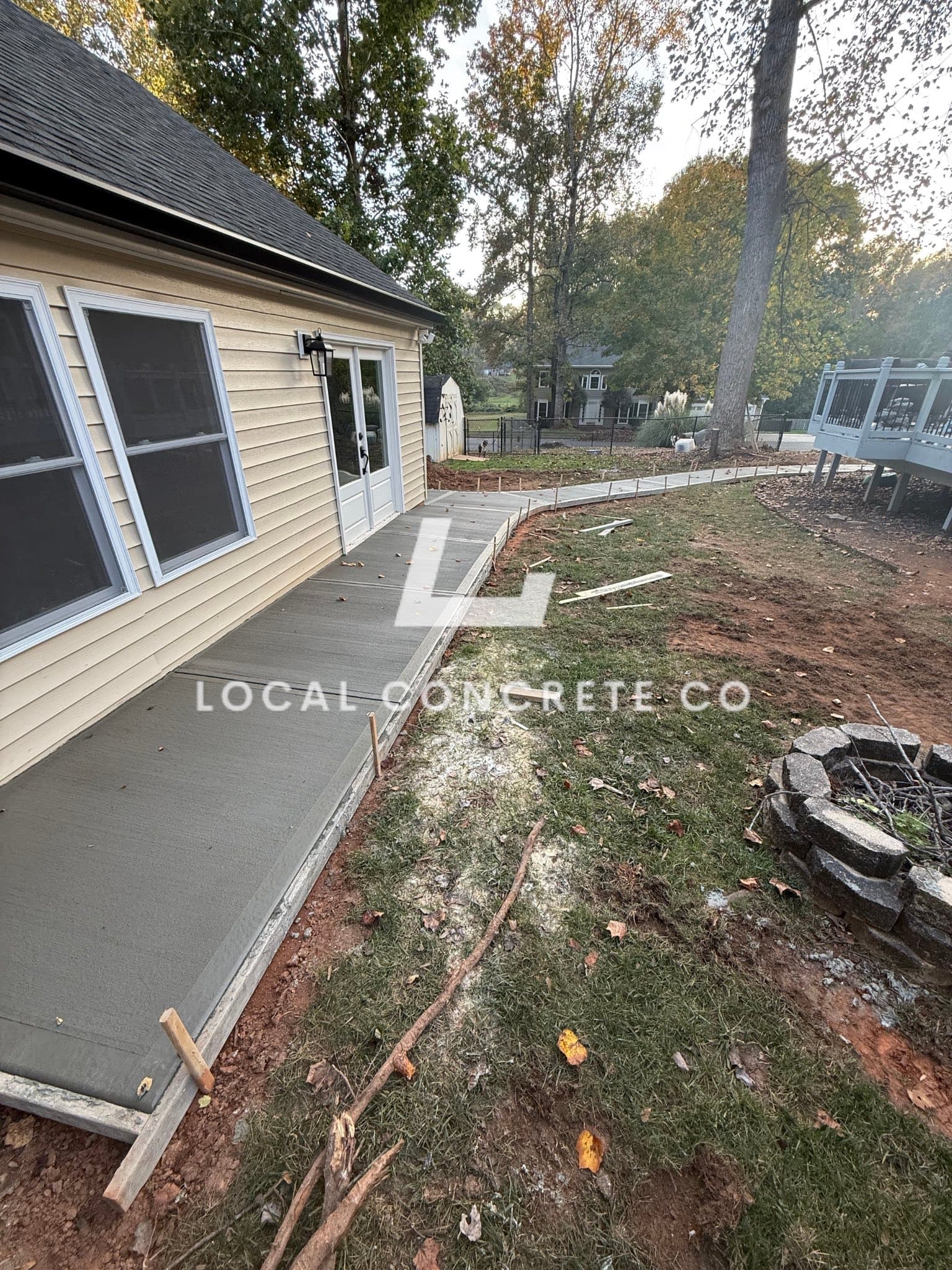
Concrete Sidewalks
Safe, code-compliant walkways for residential communities and commercial properties.

Concrete Company Services
Sidewalks carry foot traffic from the public, which means liability if someone trips and gets hurt. The most common cause of sidewalk lawsuits is vertical displacement—when one panel of concrete settles lower than the adjacent one, creating a raised edge that catches shoes and strollers. Trip hazards are defined by most municipalities as any vertical change greater than 1/4 inch. If your sidewalk has sections that have settled, cracked, or heaved beyond that tolerance, you're exposed to risk.
Preventing these problems starts with the sub-grade. We excavate deep enough to remove organic material and poorly compacted fill, replacing it with clean stone that won't settle. We also pour the concrete thick enough—typically 4 inches minimum for residential, 5 to 6 inches for commercial paths—to resist cracking from foot traffic and tree root pressure. Control joints are cut at regular intervals to manage where the concrete cracks, and we tool the edges so adjacent panels stay level even if minor settling occurs. The result is a walkway that remains safe and flat for decades.
Professional Concrete Contractor for Concrete Sidewalks
Width Requirements for Accessibility
Municipal codes typically require public sidewalks to be at least 4 feet wide, with 5 feet preferred for high-traffic areas. This ensures wheelchairs, strollers, and pedestrians can pass comfortably. Commercial properties often need wider paths—6 feet or more—especially near building entrances where people gather.
We measure and pour to the exact width specified by local code. If your property is subject to ADA compliance, we also ensure the path maintains a running slope of less than 5% and a cross-slope under 2%. These tolerances aren't suggestions—they're enforceable standards.
Eliminating Vertical Displacement
Trip hazards form when adjacent panels settle unevenly. The most common cause is poor compaction under the forms or tree roots lifting one section. We prevent this by excavating to undisturbed soil, adding a 4-inch compacted stone base, and avoiding tree root zones wherever possible.
When we have to pour near trees, we'll either route the sidewalk around the root flare or install root barriers to prevent future heaving. If a tree is too close and removal isn't an option, we'll recommend a flexible paver path for that section instead of rigid concrete.
Control Joint Spacing
Concrete shrinks as it cures. If you don't cut control joints, the sidewalk will crack randomly. The standard rule is to space joints at intervals equal to 24 to 30 times the slab thickness. For a 4-inch sidewalk, that's every 8 to 10 feet. We cut these joints within 24 hours of pouring while the concrete is still green, which encourages the slab to crack along those lines instead of across the middle of a panel.
We also cut joints at any change in direction, at intersections with driveways, and where the sidewalk meets steps or ramps.
Durable for Public Use
Sidewalks see more abuse than most concrete surfaces—bicycles, skateboards, delivery carts, snow plows. We use a denser mix with a lower water-to-cement ratio, which increases abrasion resistance. The finish is a medium broom texture that provides traction without being rough enough to snag shoes or damage wheels.
We also air-entrain the mix in climates with freeze-thaw cycles. This creates microscopic air pockets in the concrete that give water somewhere to expand when it freezes, preventing surface spalling.
Drainage Off the Path
Sidewalks should never pond water. We crown the path slightly in the center or pitch it to one side so water sheets off instead of pooling. In areas where the sidewalk runs parallel to a slope, we may need to install a small swale or edge drain to intercept runoff before it crosses the path.
Standing water accelerates freeze-thaw damage and creates slip hazards in winter when it ices over.
Interface With Street and Driveway
Where the sidewalk crosses a driveway apron, the concrete has to transition smoothly without creating a lip. We pour the sidewalk first, then form the driveway apron to match the elevation. If the sidewalk already exists, we saw-cut and remove the section where the driveway will cross, then pour a thickened apron that ties into the sidewalk on both sides.
This prevents the common problem of driveways settling away from the sidewalk and creating a gap or raised edge.
Key Features at a Glance
Everything you need to know about what makes our concrete sidewalks services stand out.
4,000 PSI Commercial-Grade Concrete
Structural strength that exceeds residential standards
Steel Rebar Reinforcement Grid
1/2-inch grid system for superior tensile strength
Proper Drainage & Slope Management
Engineered to protect your property from water damage
Crack Control Joint System
Strategic joint placement prevents random cracking
Premium Sealant Application
Deep-penetrating protection against stains and UV damage
Freeze-Thaw Resistant Mix Design
Formulated to withstand harsh weather conditions
Zero Deposit Required
Pay in stages as work is completed, not upfront
Licensed & Insured
Fully protected and compliant with all regulations
Trusted by Thousands of Clients
Join the growing community of satisfied customers
What are we building?
Select your project type.
Why Local Concrete Contractor?
- 01.Precision craftsmanship
- 02.Transparent pricing models
- 03.Dedicated project manager
- 04.Zero Deposit Required
Concrete Contractor Construction Portfolio
See the transformation. Drag the slider to reveal the restoration precision of our commercial and residential projects.
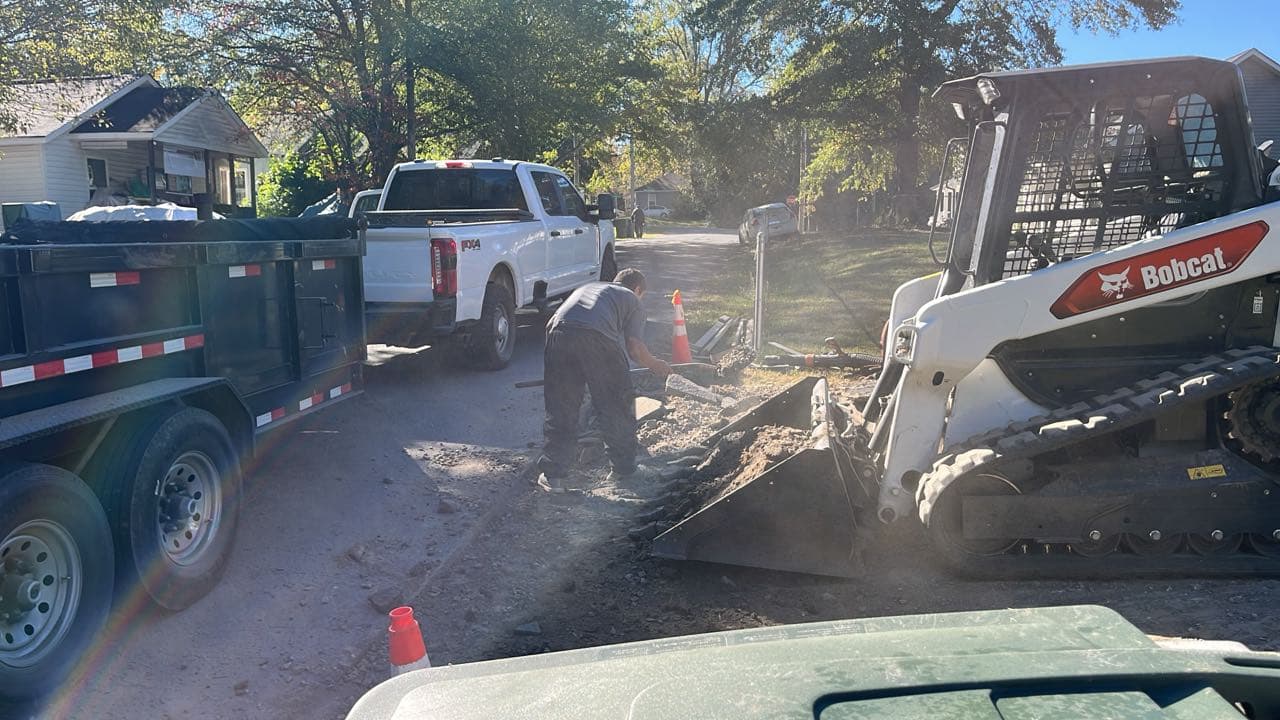

Finishing Touches in Motion
Watch our crew bring precision and artistry to the final stages of a premium concrete installation.

Building Slab
Reinforced structural foundation
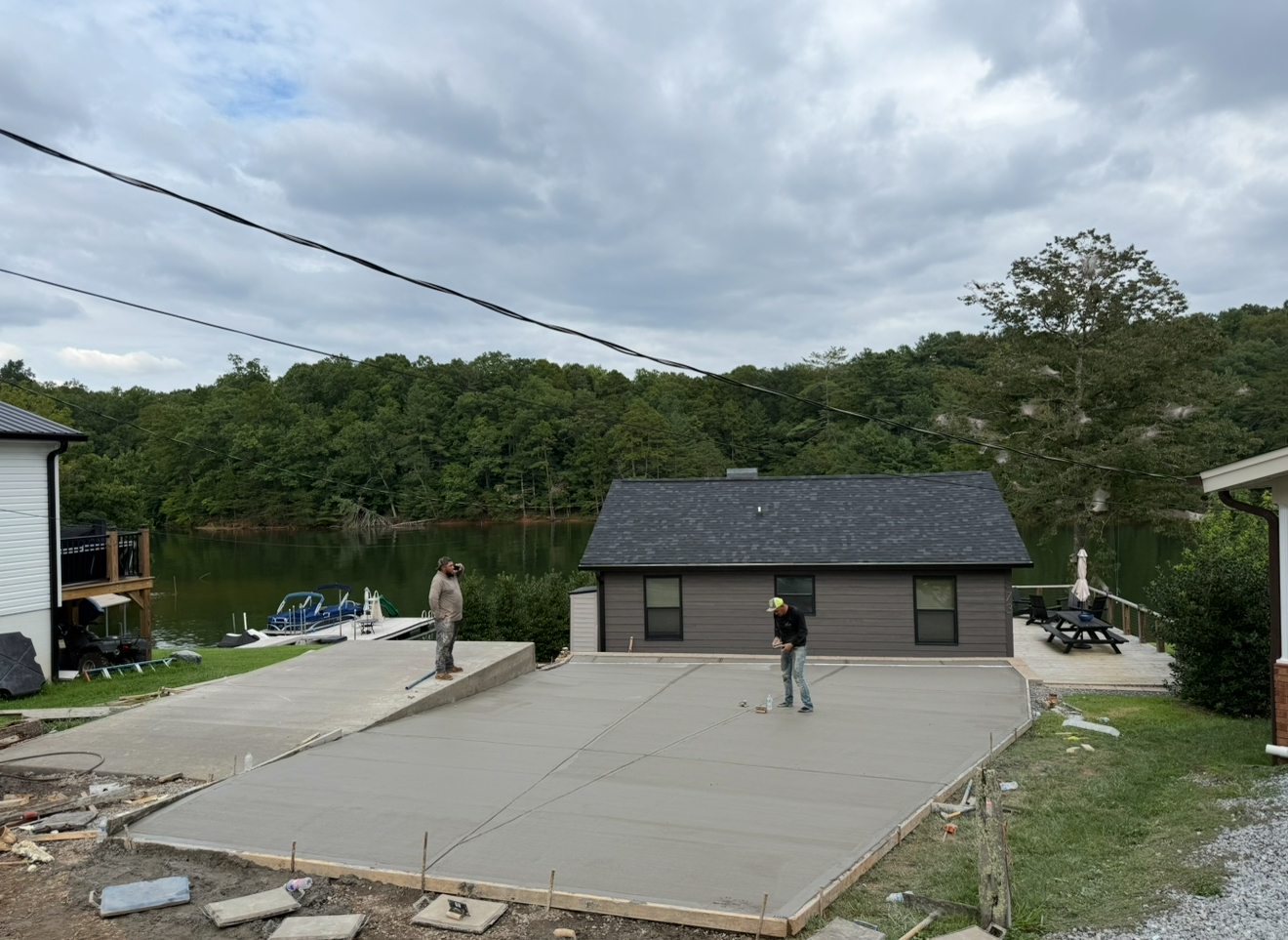
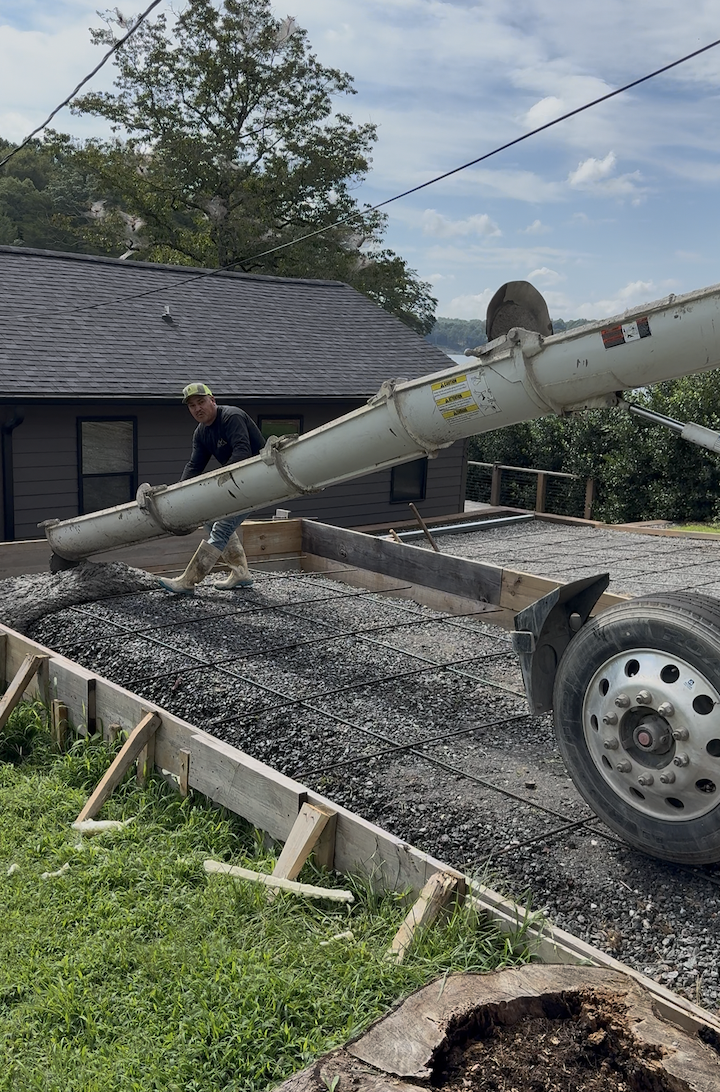



Custom Driveway
Premium residential access
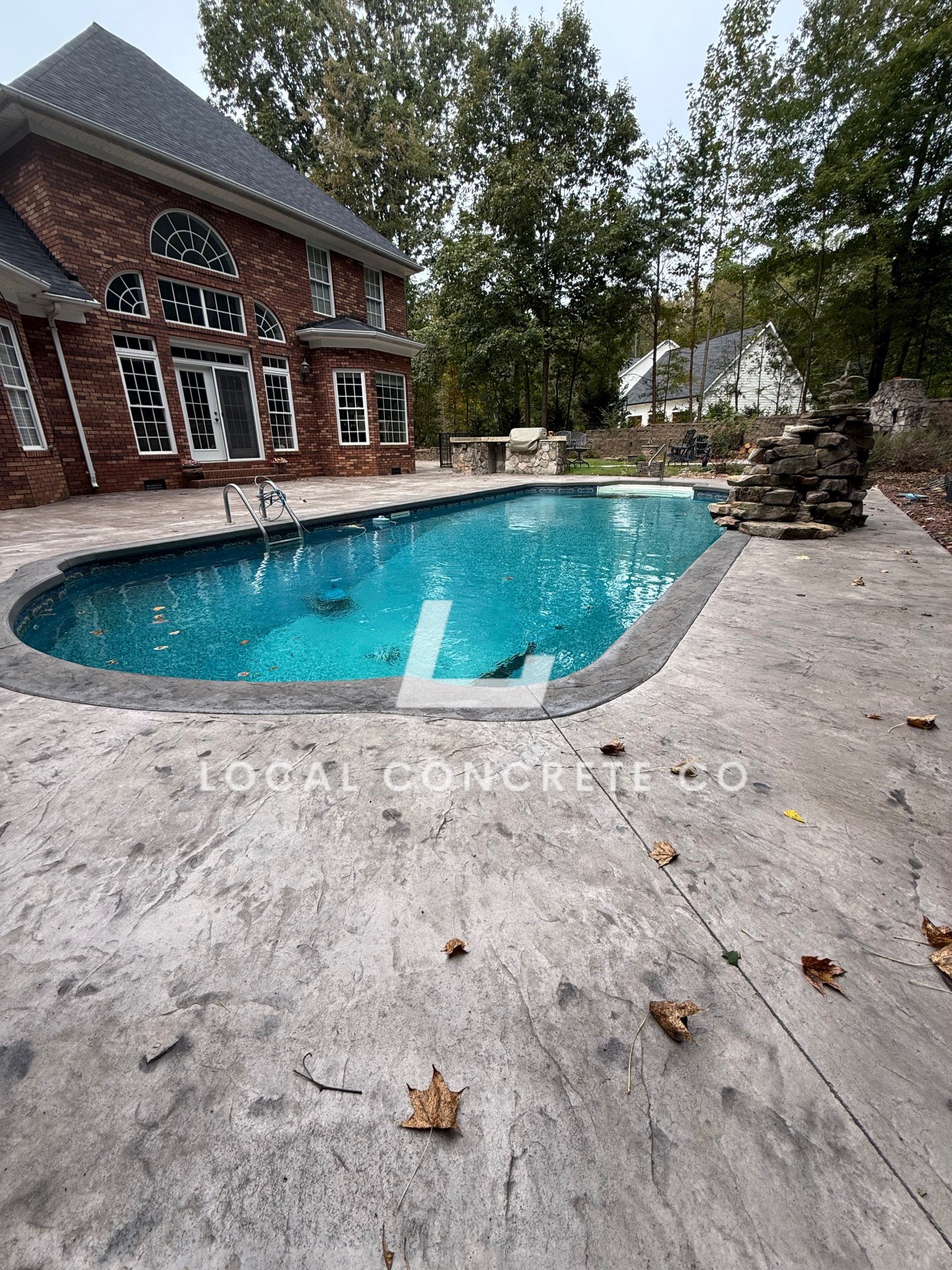
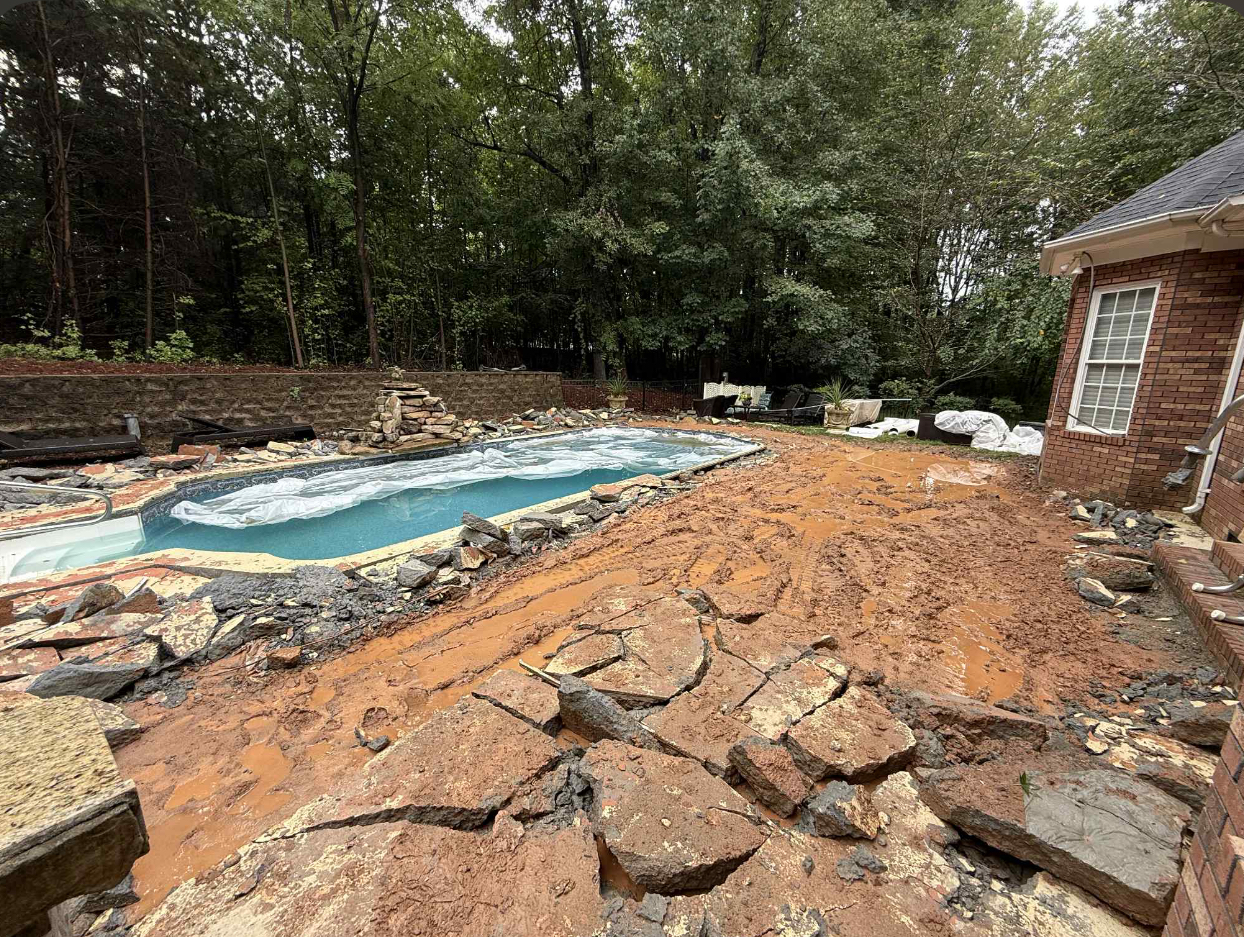



Stamped Pool Deck
Total demolition and replace